Crohn’s Disease
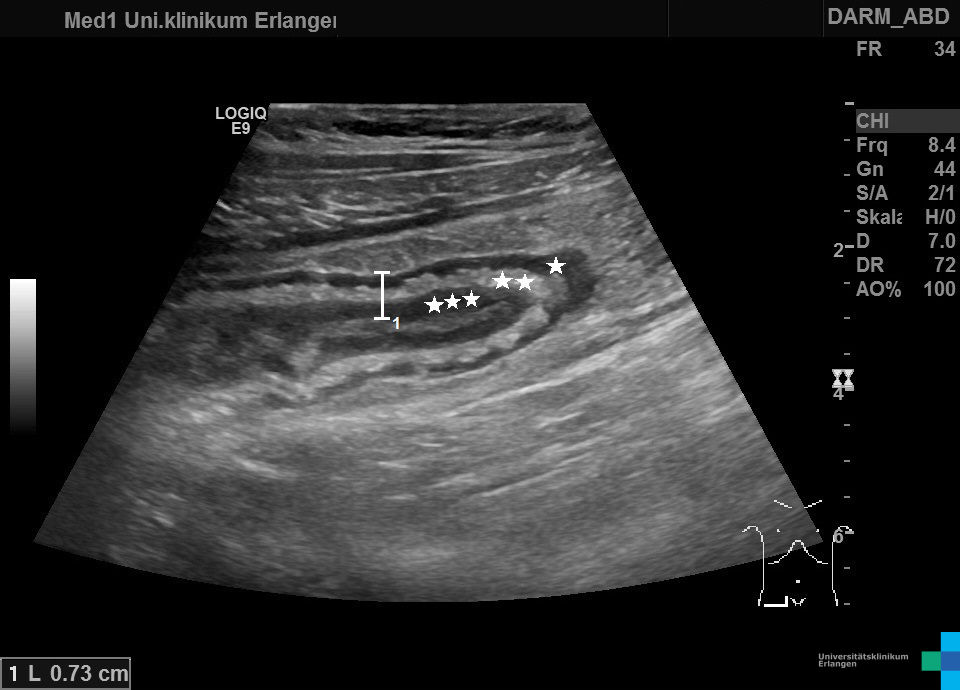
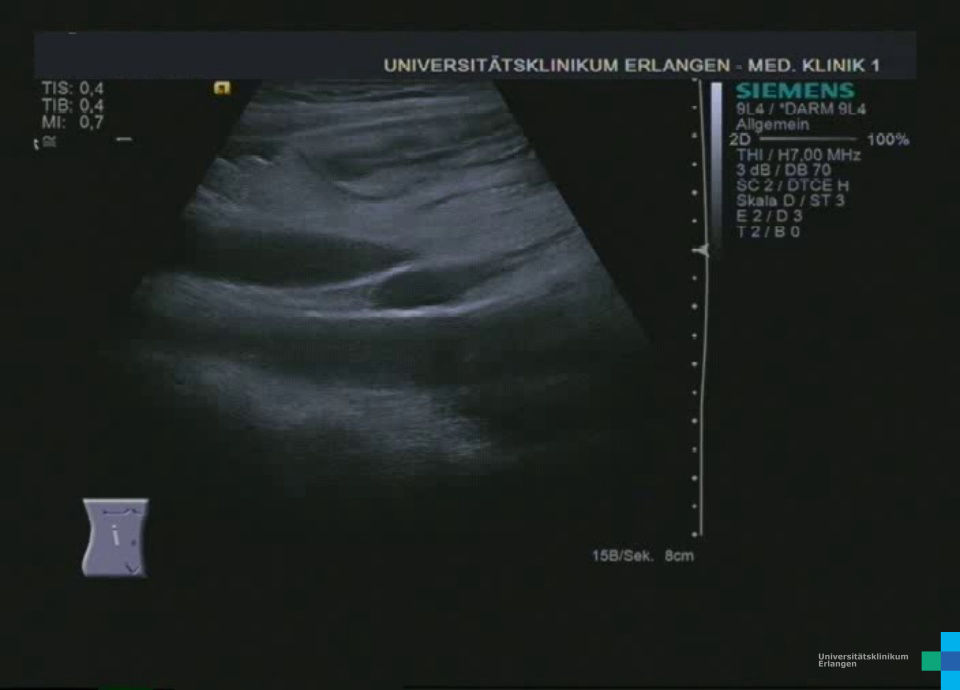
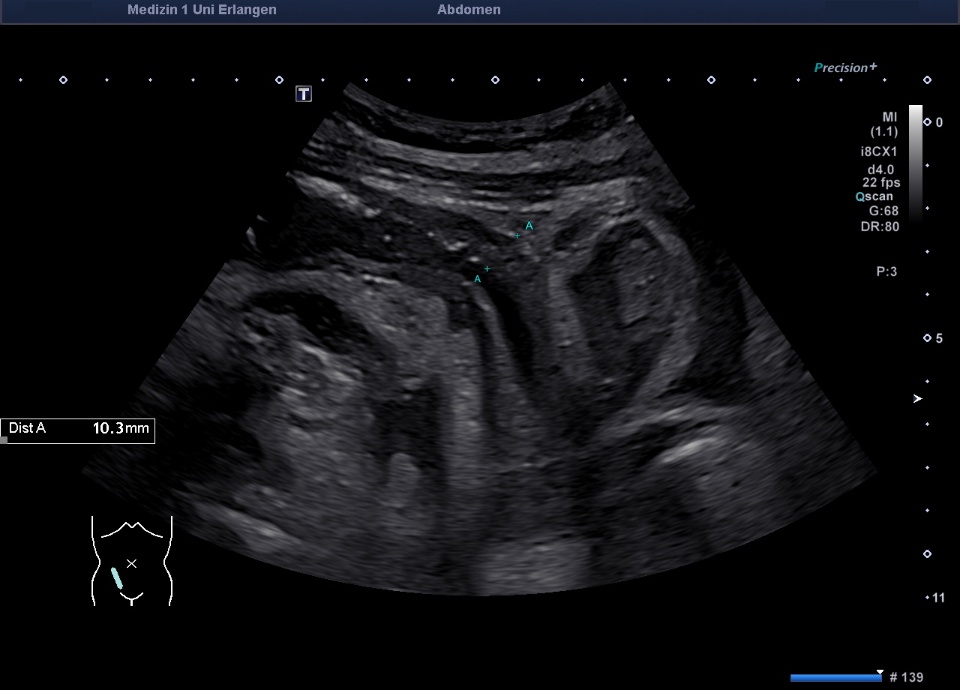
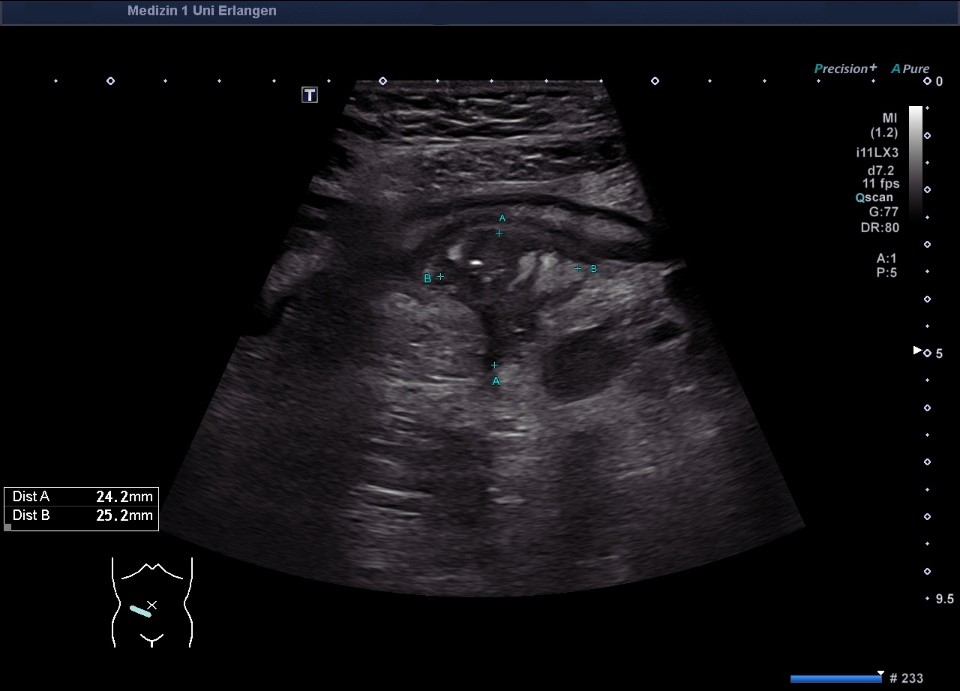
Terminales Ileum wandverdickt bei Morbus Crohn: * = Muskularis, ** = Submukosa, *** = Mukosa (hochfrequenter Linearschallkopf)
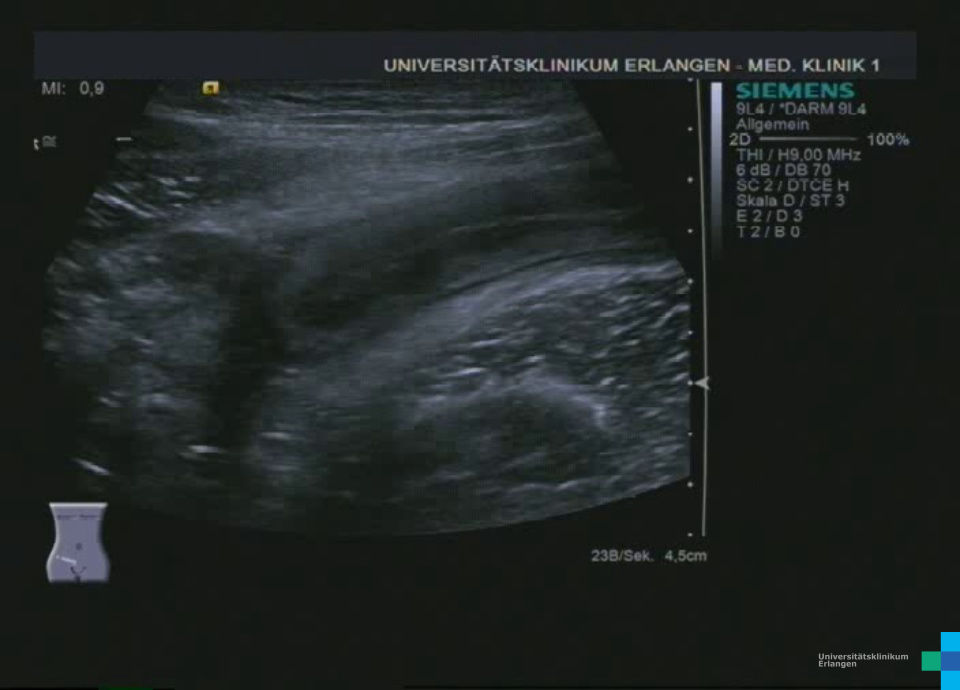
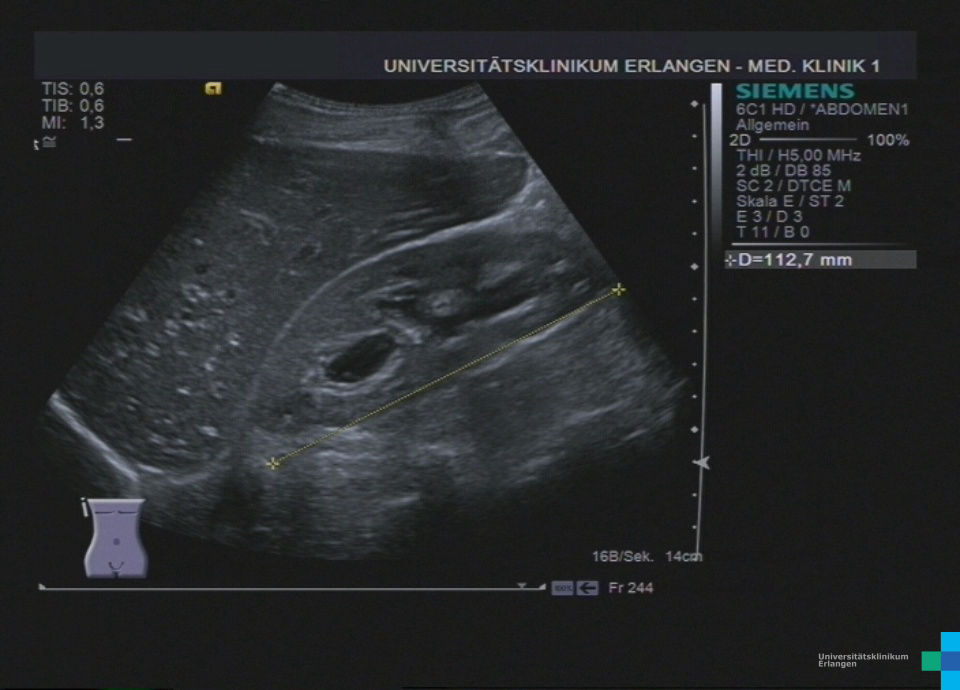
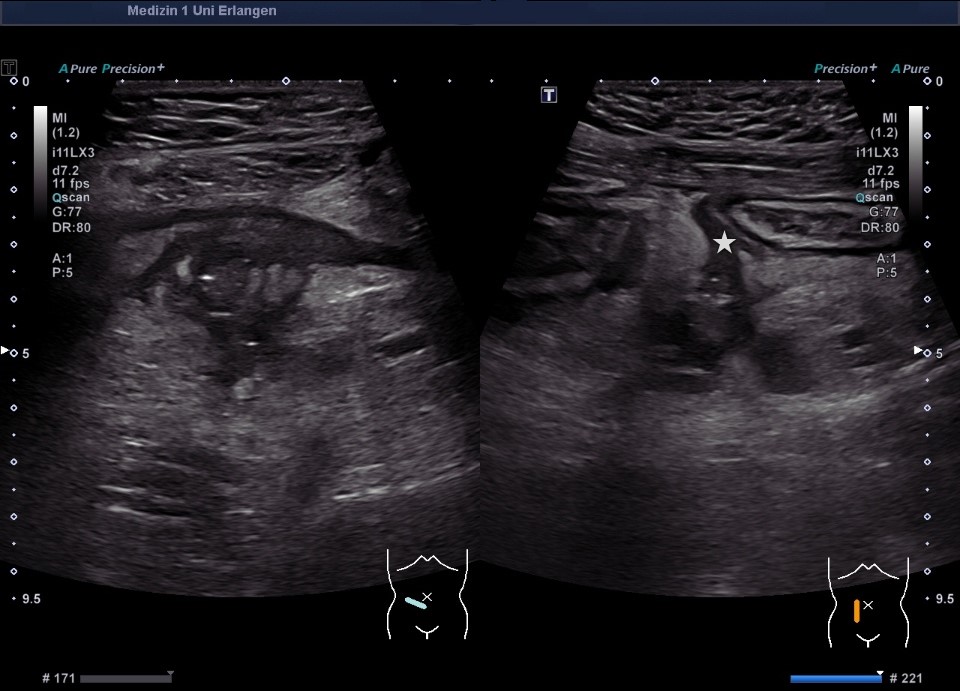
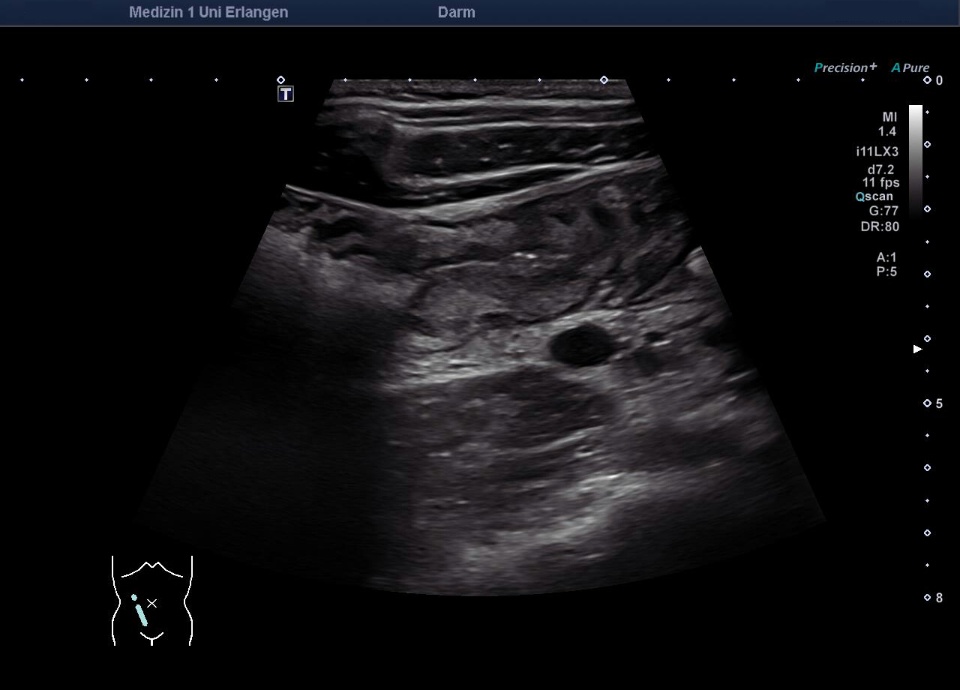
Langstreckige akute Ileitis terminals bei Morbus Crohn (Bezeichnung der Strukturen folgt im nächsten Bild; hochfrequenter Linearschallkopf)
Langstreckige akute Ileitis terminals bei Morbus Crohn (hochfrequenter Linearschallkopf)
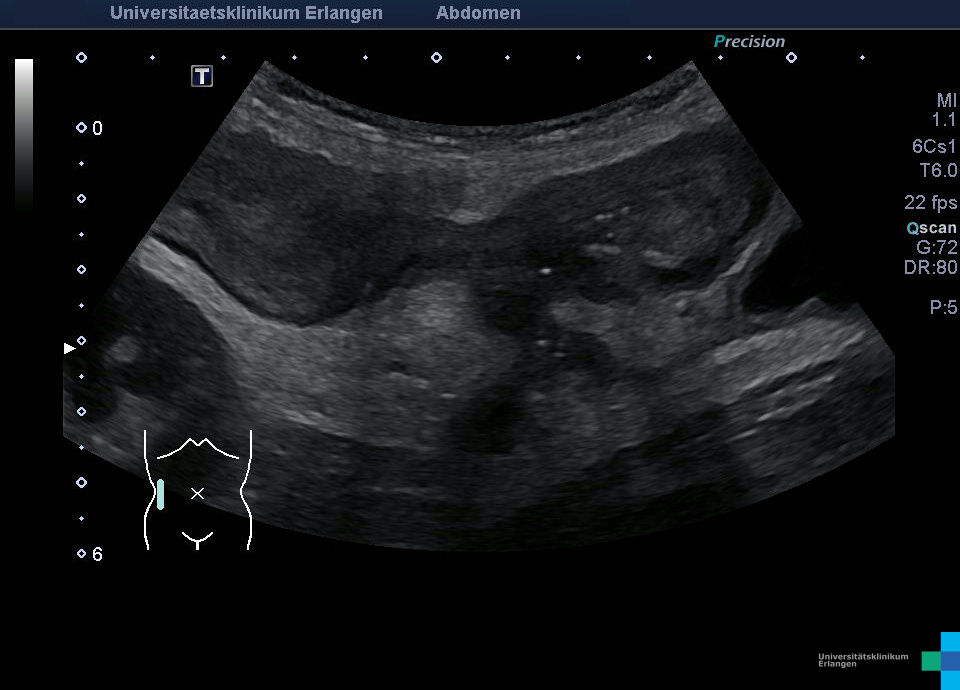
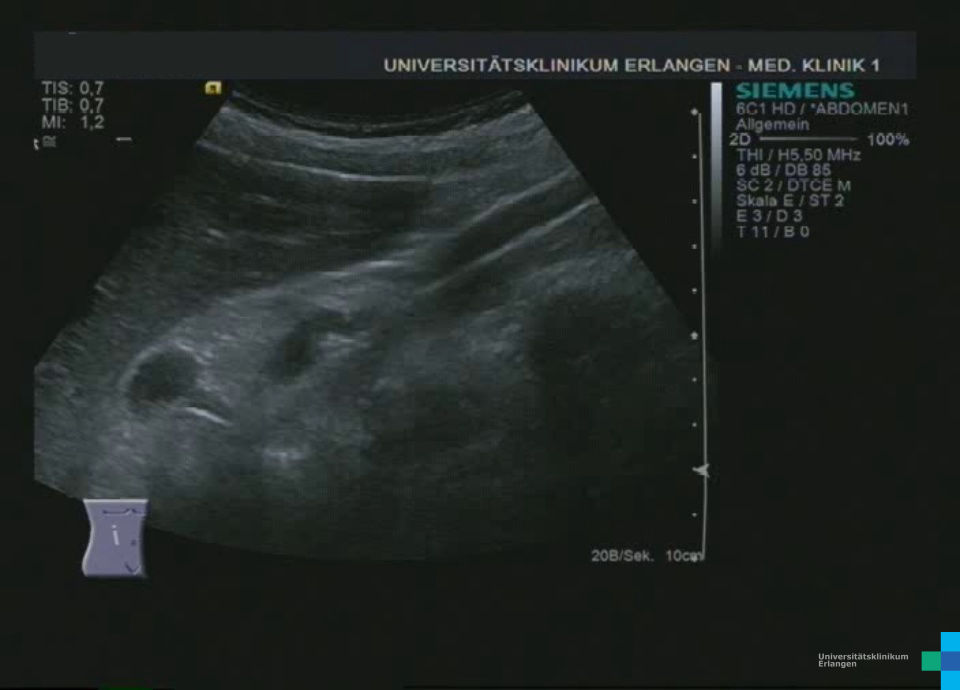
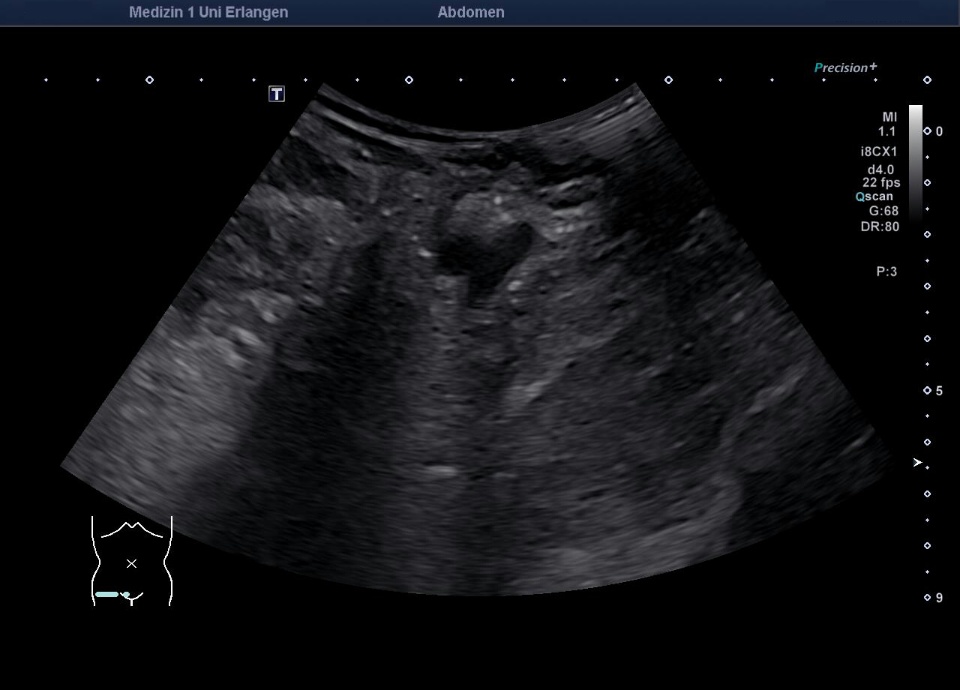
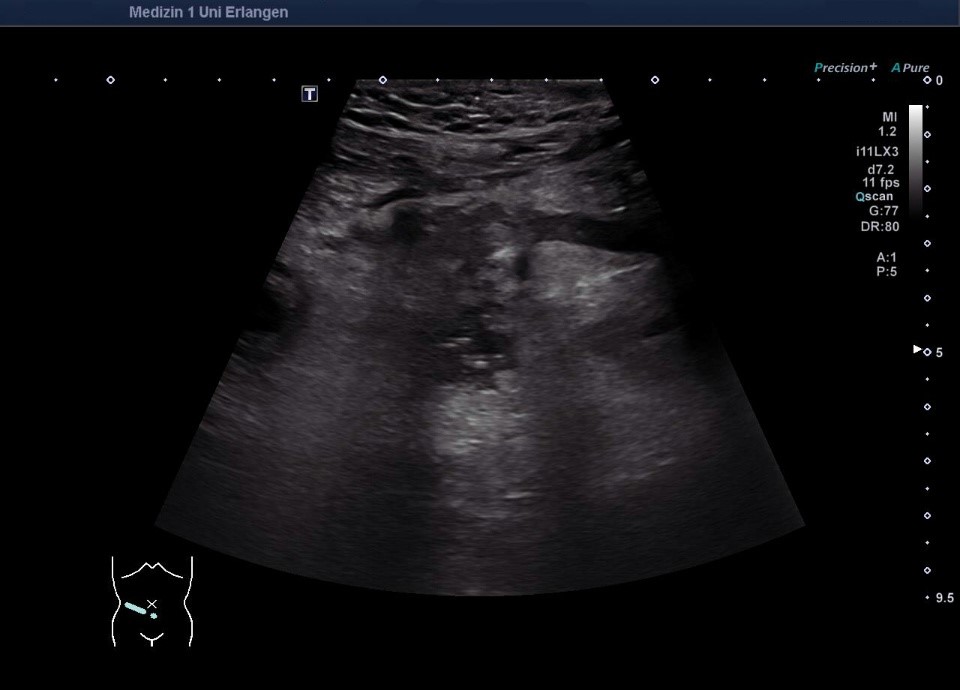
Fisteln als Komplikation eines Morbus Crohn mit echoreicher Umgebungsreaktion (Bezeichnung der Strukturen folgt im nächsten Bild)
Fisteln als Komplikation eines Morbus Crohn mit echoreicher Umgebungsreaktion (* = Fistel)
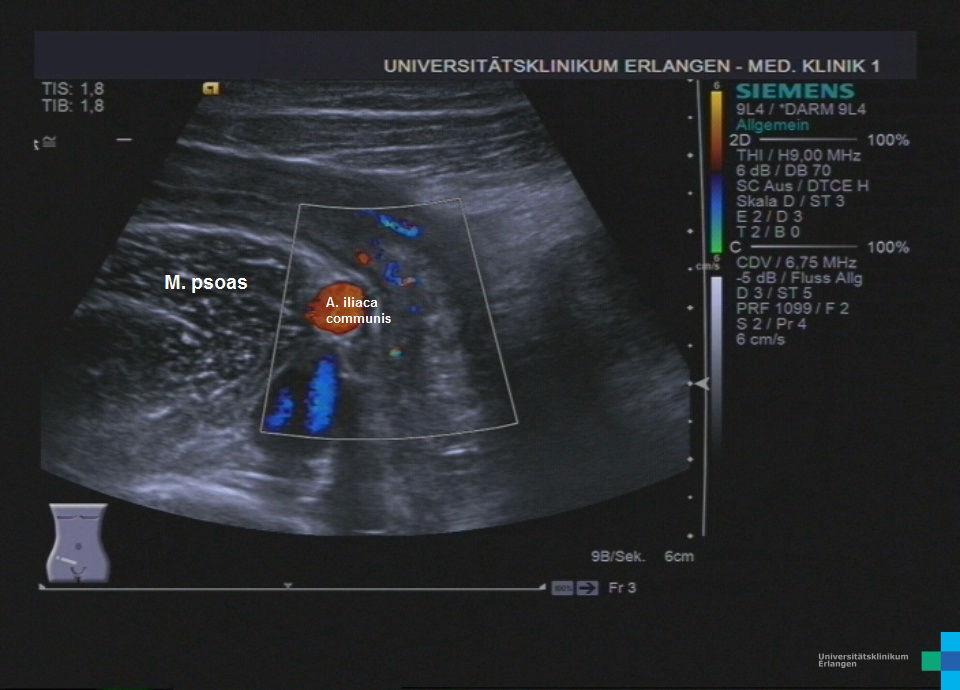
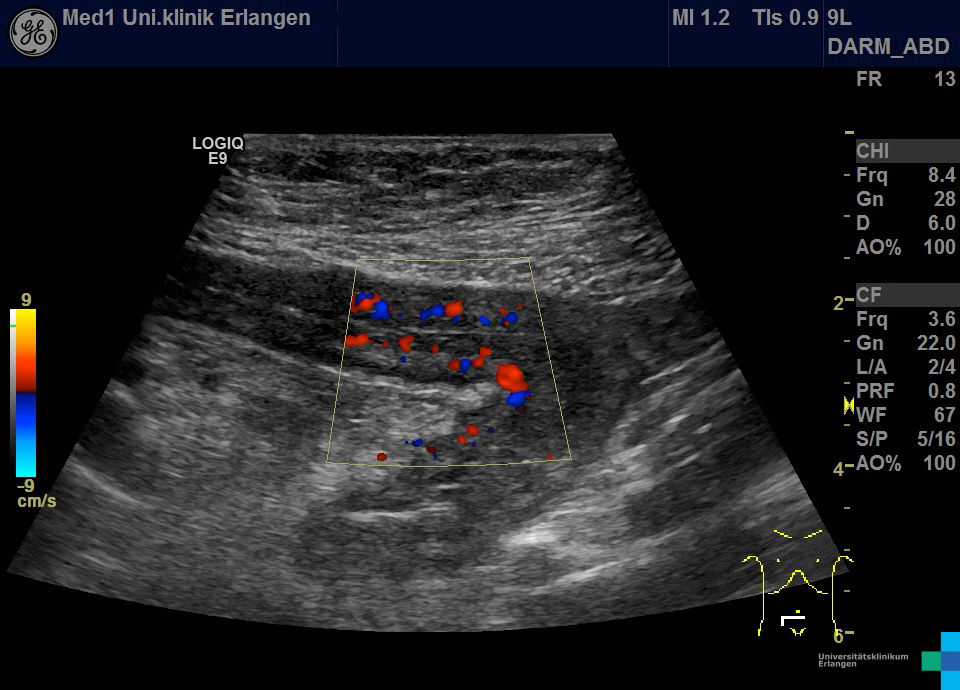
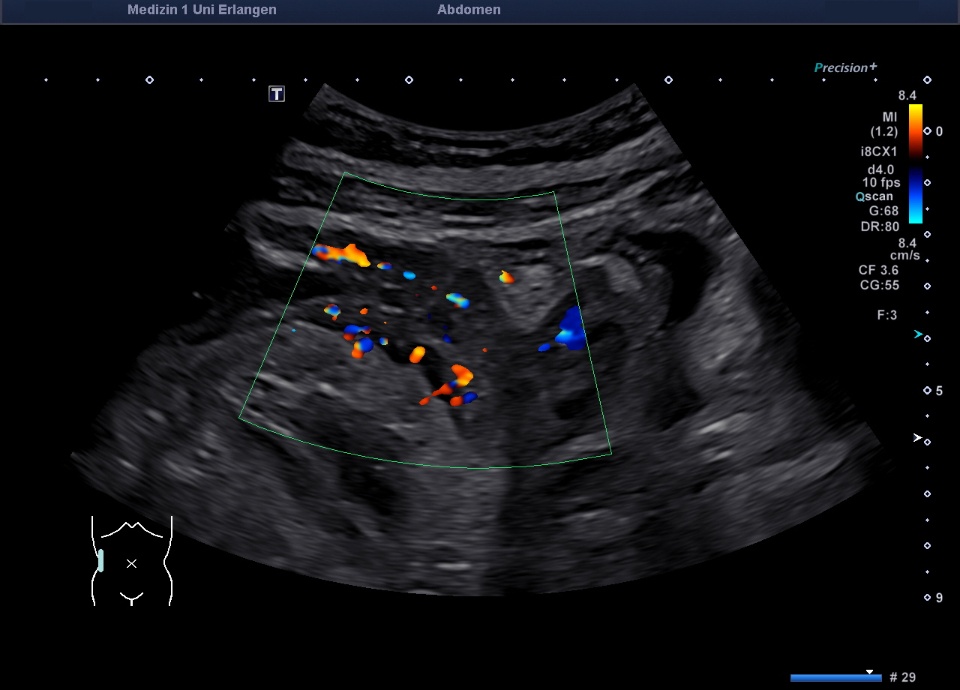
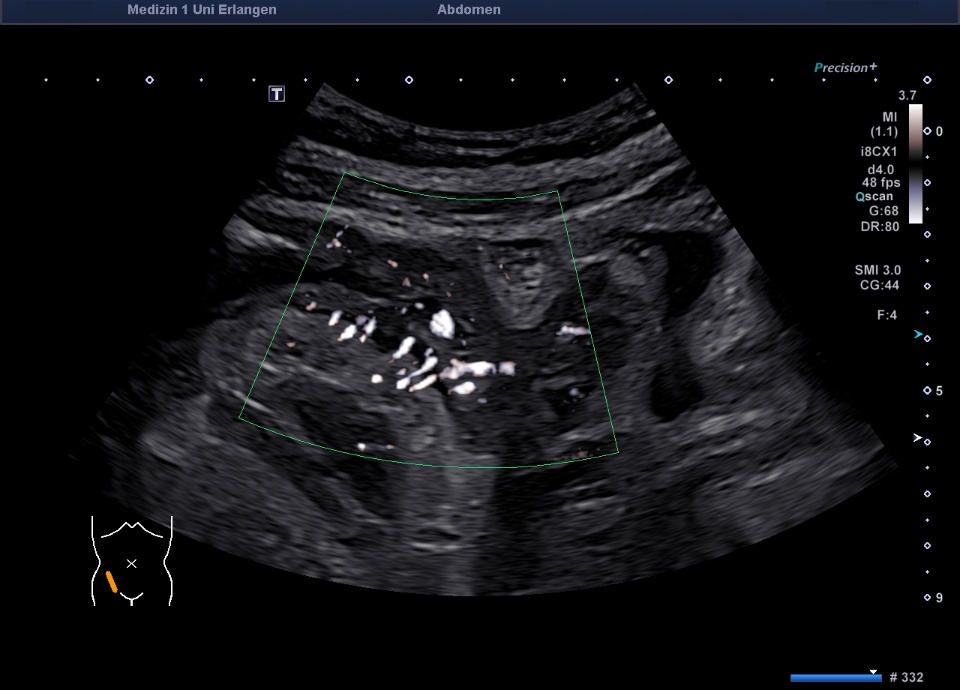
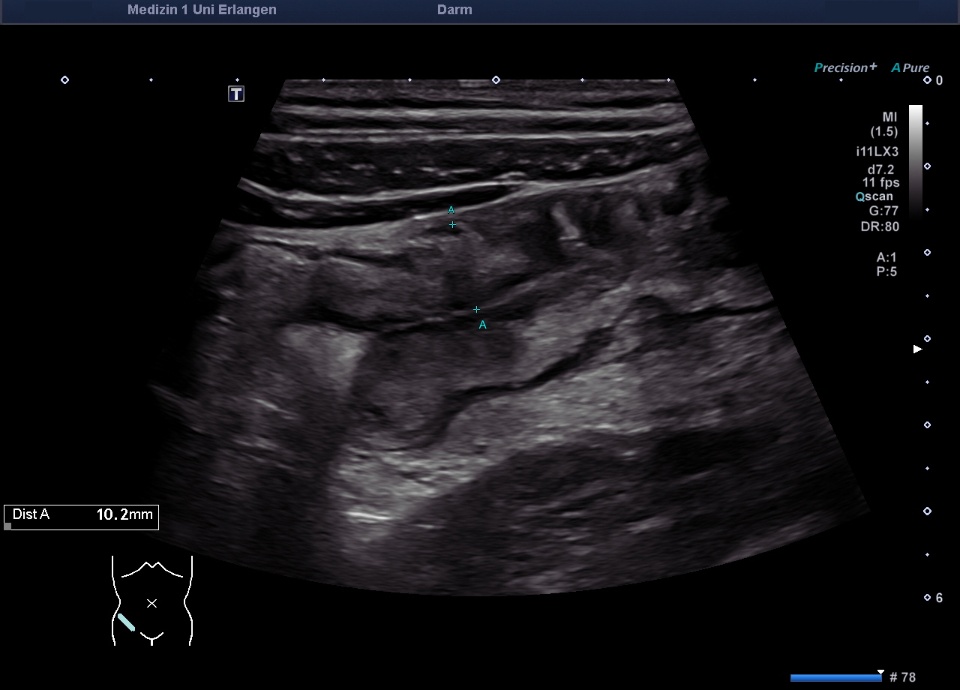
Wandverdicktes terminales Ileum – murale Hyperämie im Farb-Doppler (hochfrequenter Linearschallkopf)
Ultraschall, Ultraschallatlas, Ultraschallbilder, Ultraschallvideos, Sonographie, Sonographieatlas, Sonographiebilder, Sonographievideos, Kontrastmittelultraschall, Kontrastmittelsonographie, Medizinische Klinik 1, Uniklinik, Universitätsklinikum, Erlangen